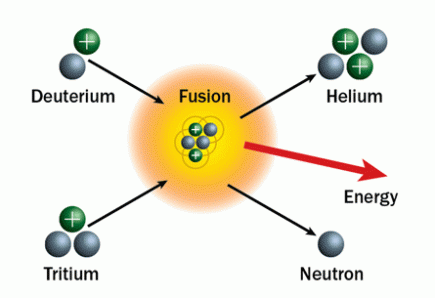
Fusion power is the power generated by nuclear fusion processes. In fusion reactions, two light atomic nuclei fuse to form a heavier nucleus (in contrast with fission power). In doing so they release a comparatively large amount of energy arising from the binding energy due to the strong nuclear force which is manifested as an increase in temperature of the reactants.
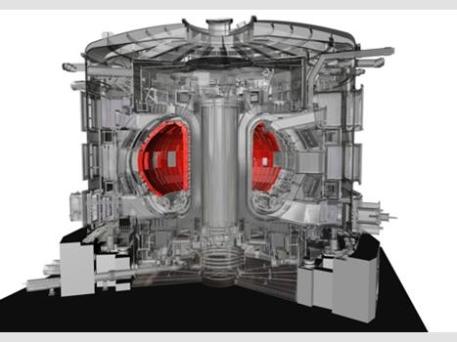
ITER NUCLEAR FUSION REACTOR DESIGN
The team at ITER based in southern France are hoping to build the first experimental nuclear fusion reactor to generate more energy than it consumes, with the aim of creating a power source that doesn’t produce carbon dioxide or large amounts of long-term radioactive waste.
The proposed blanket system that will line the inside of ITER’s doughnut-shaped 500MW tokamak reactor chamber overcomes the major challenge of how to absorb some of the 150 million °C heat that will be generated by the fusion reaction while containing the radiation produced.
The reactor will mirror the process that generates energy in the Sun: two isotopes of hydrogen are heated to extreme temperatures so they become ions (plasma) and then collided and fused together, releasing a fast-travelling neutron that transfers energy as heat.
The blanket is what will capture this energy. It will consist of 440 four-tonne modules covering a total surface of 600m2, each comprising a beryllium ‘first wall’ containing a water-cooling system to contain the plasma and absorb the heat, and a water and steel shield block to absorb the neutrons themselves.
Above image shows a fusion reactor made by teenage student named Taylor Wilson at age 14